Structure of Innovation
Many believe that innovators are born, such as some genius like Mozart. However, our experience shows that innovation is an outcome of process and not some magic. In this we should follow the thinking of the most prolific innovator of all times, Thomas Alva Edison, who said “Genius is ninety nine percent perspiration and one percent inspiration.”
The way to look at the process of innovation is that Innovation Process can be thought of as a sailboat. The hull of this sailboat is the culture of the firm, the rudder of this sailboat is the functional expertise of the firm and the mainsail represents the winds of technology driving the innovation sailboat. For a layperson, it seems that technology alone matters since she sees only the correspondence between the technology and the innovation direction. However, the hull of culture has to be strong not only to absorb the force of technology changes but also to actually move forward in the desired direction. This desired direction comes from the functional expertise of the firm, hence we term it as the rudder of the sailboat of innovation. The layperson mostly misses the importance of the hull of the culture, in the journey of innovation sailboat, unless it is starts leaking. Also, she cannot fully comprehend that the functional expertise drives the direction of innovation.
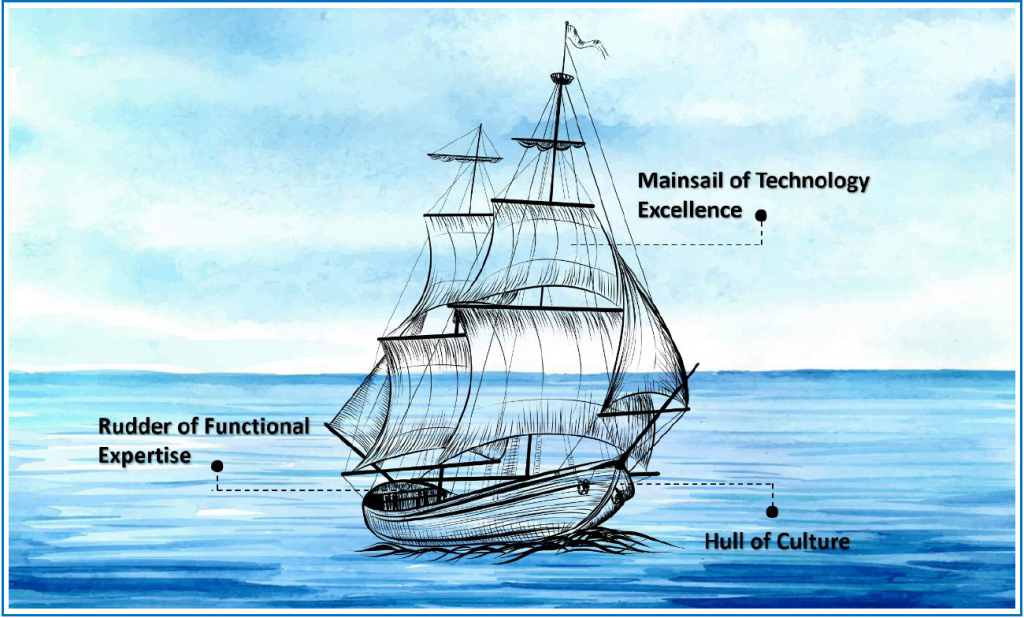
Hence, the approach to innovation should have the following three aspects:
- Cultural Aspects of Innovation
- Technical Excellence for Innovation and finally
- Functional Excellence for Innovation
The reason we should have this trifurcation is that Innovation is a never-ending process which can yield outcome on regular basis, creating value for the organization and for the society as well. This process, like any other process, needs to be thoughtfully designed and then reframed on regular basis. However, unlike other mundane processes, the process of innovation, although can prove to be an exciting journey, can feel nebulous to control on daily basis. That is because, unlike other processes, this process is deep rooted in the cultural meme of the organization. We will see now how to build culture for innovation in an organization. This process of culture will build responsible innovation which creates better tomorrow, cares for mother earth and encompasses all the stakeholders.
1. What & how of Innovation?
Innovation is an outcome driven process of developing new offering in terms of either product or service, or business process. The objective of the new offering is to appropriately meet some need of the target market which is currently either unserved or underserved or even overserved. The outcome of the innovative offering for the innovator is higher revenue and higher cash flow.
1.1 What skill sets are required for innovation which is good for humanity?
Innovation requires two basic set of human skills. First set of skills can be measured by Empathy Quotient (not be confused with emotional quotient) and second set of skills can be measured by Systemizing Quotient.
1.2 What Empathy Quotient (EQ) Measures?
EQ measures everything from the cognitive, affective, to behavioral aspects of empathy. If answers to the following questions is true for you, you have very high empathy
- Are you sensitive to others, care about them, and want to help?
- Do you listen with your heart not just your head?
- Can you hold space for others to express their people’s emotions?
- Can you listen without needing to fix someone’s problem immediately?
- Are you capable of the give and take of intimate relationships?
- Are you intuitive and sensitive to other’s needs?
- Do you care about the greater good, and the wellbeing of Earth?
However, just having very high empathy is not sufficient to produce innovation which is good for humanity. That is where skills measured by Systemizing Quotient (SQ) come into picture.
1.3 What Systemizing Quotient (SQ) Measures?
Systemizing is the skill to analyze and explore a system, to extract basic rules that govern the behavior of a system, and the ability and willingness to new construct systems. SQ measures ability to find underlying ability to systemizing.
1.4 Why both EQ and SQ are required?
Having very EQ as a unidimensional trait can make a person too sensitivity and hence unable to produce any lasting positive commercial outcome from her ability as an Empath. On the other hand, having very high SQ as a unidimensional trait can make a person create systems which have no immediate commercial reverence.
Do not get me wrong, a person with high EQ has a great role in a society, maybe as a politician, maybe as a marriage counselor and so on. Similarly, a person with high SQ has a role in a society as a mathematician, as a scientist, and so on.
However, for commercial innovation which has positive impact on society one needs to have both skills present in the organization which is undertaking the innovative activity.
An organization full of high SQ people will produce a lot of innovation which will increase the profits of the company, say be producing more addictive sugary waters or by cutting corners in environmental safety to reduce costs.
An organization full of high EQ people will be able to appreciate the needs of their stakeholders deeply and correctly. However, without ability to analyze the root causes and design new solutions they will not be concretely address the needs that they have discovered.
2. How Innovation can be made easy?
Innovation is not difficult if it is thought of as process that anyone can do with practice. There was a time about 700-800 years ago, only a handful of mathematicians in Europe had learnt of multiplication techniques developed in India to multiply large numbers quickly. Now, every nine-year old child is exposed to the same technique as a matter of process of getting literate.
Similarly, innovation is a technique. It can be taught. It can be learned. It can be mastered.
2.1 What are the steps of innovation?
Innovation involves the following steps
- Understanding the unmet or overmet needs by current offerings in the market
- Questioning the underlying assumptions behind current offerings in the market
- Use current technology roadmap which was not available when the offering was last iterated in the market
- Construct the offering anew
- without regard to Received wisdom,
- based on laws of universe as applicable to the situation,
- by expanding the realm of possibility by infusing new technology available now
2.2 What are the fountains of ideas for Innovation?
The following are some of the sources of innovations
- For process innovations, errors reported and the Corrective Action/ Preventive Action/ Remedial Action analysis is a great source of ideas for innovations
- For Product and Service Innovations, Jobs To Be Done framework is a great source of ideas for innovation
2.3 What is the role of grit in Innovation?
Psychologist Angela Lee Duckworth says: “Grit is sticking with your future — day in, day out, not just for the week, not just for the month, but for years — and working really hard to make that future a reality.”
Innovation is nothing but shaping the future in some novel way by bringing in new offerings to the market. It goes without saying, the people and the organizations who are willing to stick longer with their preservation to shape their future, have higher chances of being innovative.
2.4 Do we have to be genius to be innovative?
Innovation requires directed creativity. However, this directed creativity requires a set of defined skills and behaviors, all of which can be taught and practiced.
Organizations can teach themselves to listen to their stakeholders more openly and hence increase their “EQ”. Similarly, organizations can practice documenting every step of their business and can teach themselves to have higher “SQ”. Finally, organizations can hire individuals with grit who will not say no in face of difficulties.
Hence one does not have to be born genius to be innovative. Or organizations do not have to search for next Steve Jobs like genius to become innovative. In fact, if an organization has to produce innovation regularly, with less uncertainty and with higher chances of profits, then innovation has to be to a teachable skill-and-behavior-based process. Conversely, if an organization depends on a set of geniuses then the innovations will come in unpredictable waves, and after the genius moves on, the organization has to live off her legacy, as can be seen at Apple – after death of Jobs they have not launched any blockbuster new category in nearly a decade, but just fortified their existing products. A decade before death of Jobs, Apple created three new categories – iPods, iPhones and Macbook Air. Are those categories valuable? Surely yes! But are those categories outcome of repeatable process? No. One cannot wait for a once a century “Jobs” to crank their innovation. It can be a machine-like process as companies like 3M have shown us time and again.
2.5 What thinking process is required for Innovation?
There are two ways of thinking. First type of thinking is first principles thinking where you look at a problem solely on its merit and evaluate the same from your knowledge of how the world should work – say basic rules of physics, chemistry, microeconomics etc. Second type of thinking is analogical thinking. In analogical thinking, we do pattern matching. First principles thinking is required when you want to make an order of magnitude change in the world around you. While analogical thinking is useful when you are searching for incremental changes to a known solution. Analogical thinking can be automated and is already largely automated in the form of traditional programming and also AI. However, if you apply pure analogical thinking, success is not assured, as the background assumptions are not tested for validity. Not checking all the underlying assumptions can lead to innovations which do not click in marketplace.
3. Why is Innovation important?
Existing Human knowledge is scattered and unevenly distributed. Just as an example, artic Belgium produces 500,000 kg of tomato per hectare, cold Iceland 350,000, arid Palestine 150,000, mediterranean Greece 60,000 and India 24,000. That means the current best in the world is 20x more productive than India. And similar trends are true for different countries for all products and services. If all countries in the world try to achieve the top quartile productivity with various innovative methods for all food products, world hunger will disappear. If all countries achieve Cuba or Japan’s levels in healthcare, the world will be healthy place. And so on. All these improvements require application of existing technologies in innovative ways. No new pure science development needed for 20x growth in food production, if we are innovative!!!!
If fact, we cannot consume 20x more food. This means, we can return something like 90%+ of farmland to forests if we are innovative in farming alone. That will heal mother nature on one hand and reduce house prices on other hand by making more land available for free for house building.
Similar examples can be developed for all industrial products as well as services. Also, the new products and services that can be developed through innovation have similar limitless possibilities of improving human conditions.
4. Why is Innovation Possible?
Simply stated, innovation is possible because future is not written yet. The future will be shaped by our thoughts and our actions today. Most of the products and services that human race is destined to enjoy in future are yet to be designed. Why I am saying so? Just look around you. Count the products and services that you have consumed in last six months. How many of those were available to our forefathers just 200 years ago in the current form? Hardly a few. So, our forefathers had not consumed most of the things that we are enjoying. Similarly, in fact, at higher pace, our grandchildren will enjoy products and services that we have not yet dreams of. We have to just keep dreaming those into existence yet!
5. Putting it all together – Innovation and Society Revisited
We have seen that innovation requires a unique mix of culture, namely set of skillsets and behaviors as defined by EQ, SQ and Grit. With EQ, you can create synergies with all the stakeholders. With SQ you can build on the desires of the stakeholders and build sustainable offerings. We also have seen that just innovative approach can improve human conditions significantly even with existing technologies. That will bring better future for humanity.
